Hello and welcome to the exciting world of Data Structures and Algorithms (DSA) using C++. 🌟
In this journey, I'll dive into the fundamental concept of tree
Unraveling Trees in DSA
What Are Trees?
In the world of data structures, a tree is a hierarchical structure resembling a real-world tree turned upside down. It consists of nodes connected by edges. At the top, we have a single node called the "root," and the remaining nodes are divided into subtrees.
Now, let's venture into some intriguing types of trees:
Binary Tree
A Binary Tree is one of the most fundamental tree structures. It has, as the name suggests, two branches: a left child and a right child. Each node can have at most two children. It's like a family tree where each individual has at most two descendants.

Ternary Tree
Expanding on the binary tree concept, a Ternary Tree allows each node to have up to three children. This tree structure broadens the possibilities and can be likened to a family tree with more complex relationships.

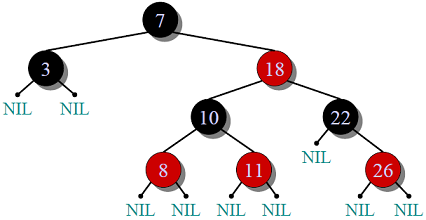
Red-Black Tree
The Red-Black Tree is a self-balancing Binary Search Tree, where each node has a color either red or black. This coloring scheme ensures that the tree remains approximately balanced, facilitating efficient searching and insertion operations.
AVL Tree
The AVL Tree is another self-balancing Binary Search Tree that maintains its height to be logarithmic, ensuring that all operations (insertion, deletion, search) have a time complexity of O(log n).

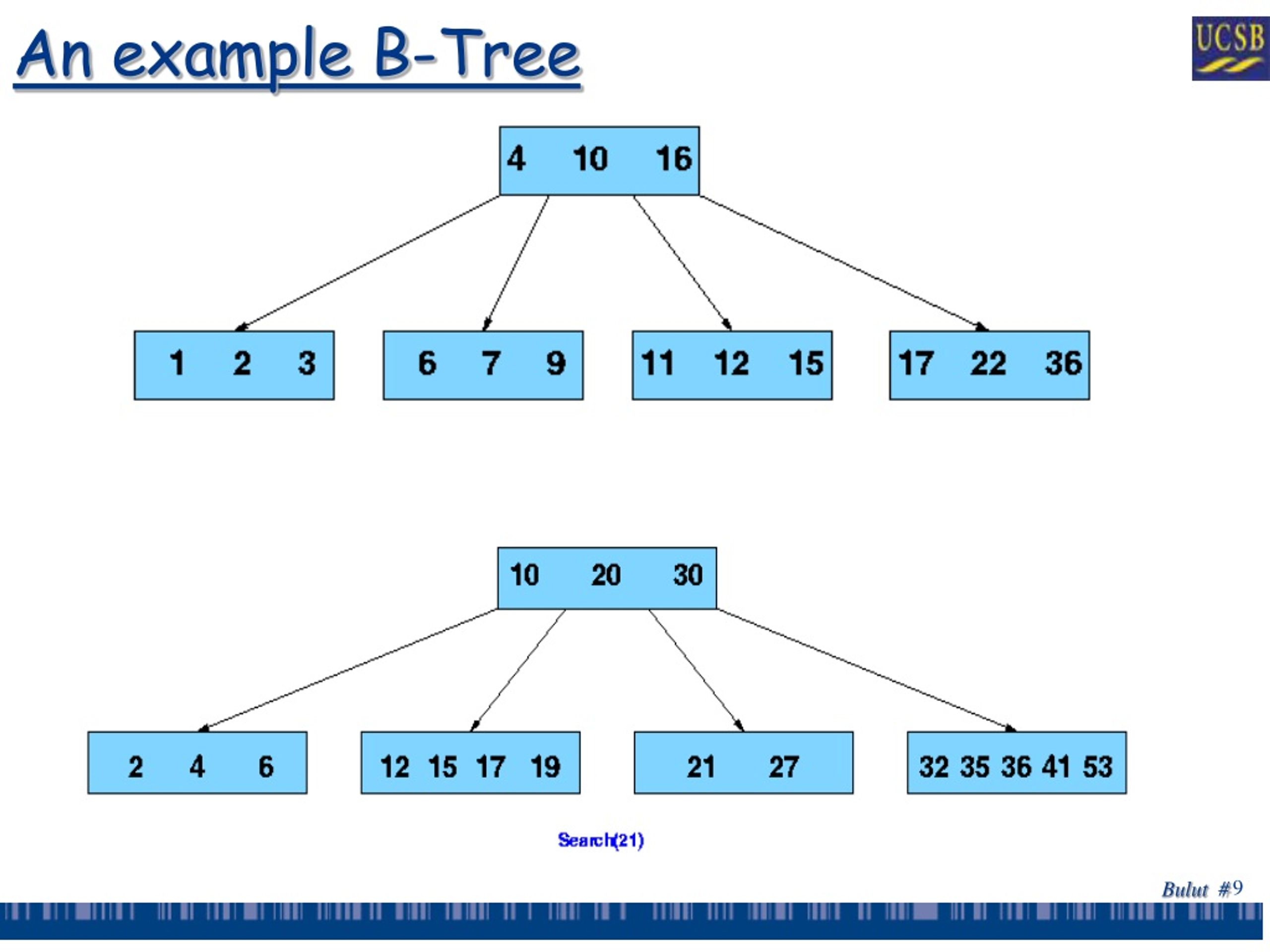
B-Tree
A B-Tree is a more complex tree structure often used in databases and file systems. It's designed to handle large amounts of data and ensures fast access and insertion operations.
Tree Terminologies
As we journey deeper into the forest of trees, let's grasp some essential terminologies:
Node: The fundamental building block of a tree.
Root: The topmost node of the tree.
Branch: The connection between nodes.
Subtree: A smaller tree within the larger tree.
Descendant: A node connected by a path to a higher node.
Path: The route between nodes.
Ancestor: A node connected to a lower node by a path.
Depth: The level at which a node is situated.
Level: The generation or distance from the root.
Height: The length of the longest path to a leaf node.
Formula for Height: Height of a tree = max(Height of left subtree, Height of right subtree) + 1.
Special Kinds of Binary Trees
Now, let's explore some specialized binary trees:
Half Binary Tree: A binary tree in which every node has either 0 or 2 children.
Full Binary Tree: A binary tree in which every node has 0 or 2 children.
Perfect Binary Tree: A binary tree in which all internal nodes have exactly two children, and all leaf nodes are at the same level.
Balanced Binary Tree: A binary tree in which the depth of the left and right subtrees of every node differ by at most one.
Certainly, let's dive deeper into the concepts of half binary trees, full binary trees, perfect binary trees, and balanced binary trees:
Half Binary Tree:
A Half Binary Tree, also known as a Strict Binary Tree, is a type of binary tree where each node has either 0 or 2 children. In other words, there are no nodes with just one child. It's a more structured and balanced form of binary tree.
The term "half" here indicates that each node is "full" in the sense that it either has no children (0) or has two children (2). There are no nodes with only one child.
Half Binary Tree Example:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \
4 5
In this example, every node either has no children (e.g., node 3) or has two children (e.g., node 2).
Full Binary Tree:
A Full Binary Tree, also known as a Proper Binary Tree or 2-tree, is a type of binary tree where every node has either 0 or 2 children. In other words, there are no nodes with just one child, similar to a half binary tree.
A full binary tree is characterized by the fact that all its internal nodes (non-leaf nodes) have exactly two children. This property gives it a highly balanced structure.
Full Binary Tree Example:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
In this example, every internal node (1, 2, and 3) has exactly two children.
Perfect Binary Tree:
A Perfect Binary Tree is a specialized case of a full binary tree. In a perfect binary tree, all leaf nodes are at the same level, and every internal node has exactly two children.
This structure ensures that the tree is completely filled, meaning there are no missing nodes at any level. Perfect binary trees are often used in applications where a balanced structure is crucial.
Perfect Binary Tree Example:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
In this example, all leaf nodes (4, 5, 6, and 7) are at the same level, and every internal node has exactly two children.
Balanced Binary Tree:
A Balanced Binary Tree is a more general concept. It refers to a binary tree in which the depth of the left and right subtrees of every node differs by at most one. In other words, the tree is as balanced as possible.
Balanced binary trees are crucial for ensuring efficient search and retrieval operations. Various types of balanced binary trees, such as AVL trees and Red-Black trees, are commonly used in computer science and data structure applications.
Balanced Binary Tree Example:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ \
4 5 6
In this example, the depth of the left and right subtrees of every node differs by at most one.
Understanding these types of binary trees is fundamental for optimizing data structures and algorithms in various applications. They offer efficient ways to organize and manage data, making them valuable tools in the world of computer science.
Branching Out
As I conclude this session, remember that understanding tree structures is a foundational step in mastering DSA. Trees are not only fascinating but also a powerful tool for solving complex problems efficiently.
So, stay curious, keep exploring, and don't hesitate to experiment as you progress on your learning journey. In the next session, we'll delve into implementation of tree
Happy coding! 🚀🌳🌲
Stay tuned for my next session! 🌟
